// Video Surveillance
Video Analytics: Adding Steak to the Sizzle

Video Analytics:
Adding Steak to the Sizzle
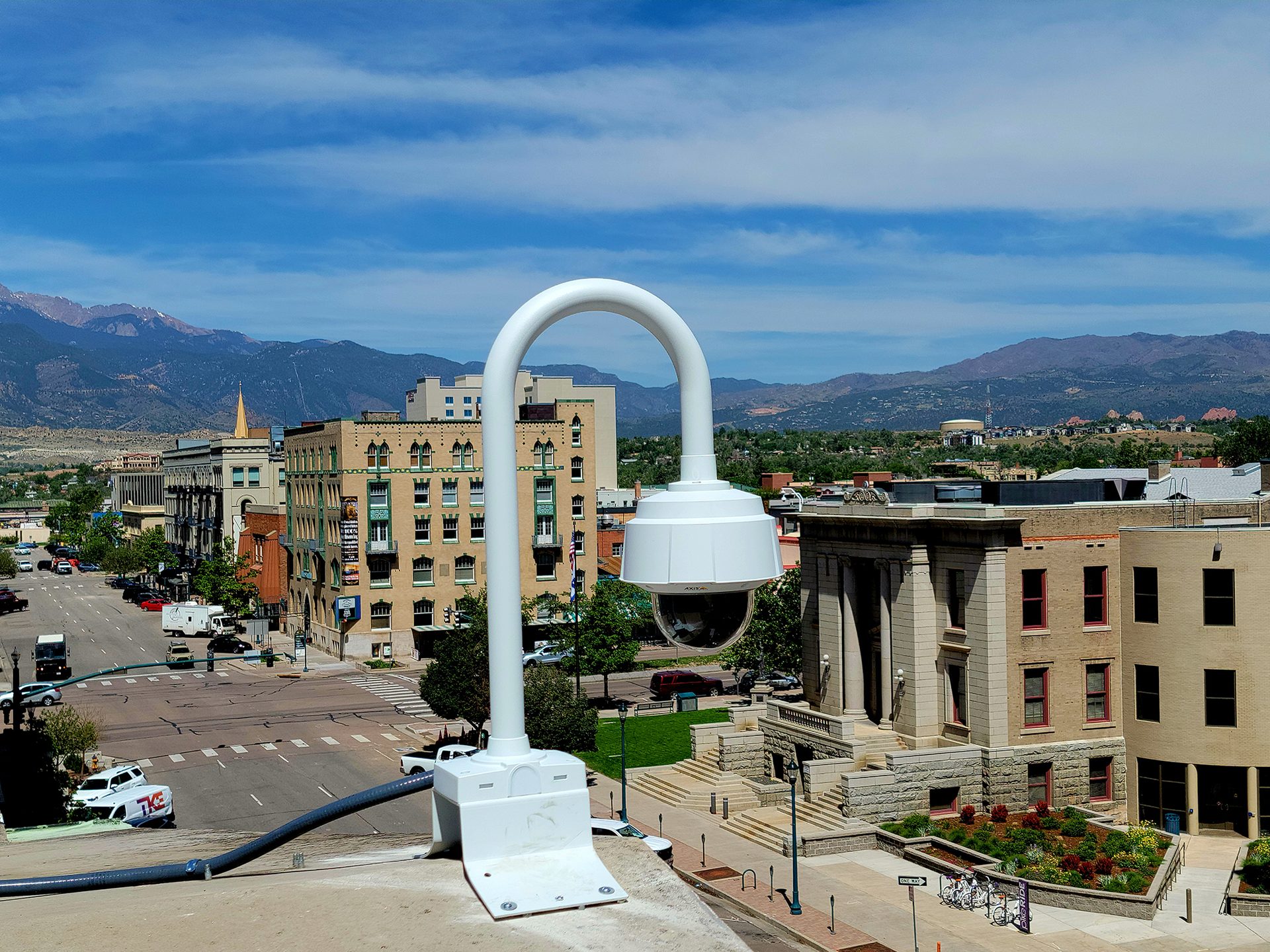
Cameras with processing capabilities at the edge are part of the reason why the demand for video analytics has grown dramatically over the past few years. Cameras are used to drill down on events or slew to cue, typically triggered by an application-specific analytic or event. Pictured is a moveable camera as part of a city-wide surveillance system in downtown Colorado Springs, Colo.
IMAGE COURTESY OF STONE SECURITY
While a global pandemic created new needs for video analytics beyond security, a burst of tech advances made it more sophisticated. Learn how businesses are finding more uses for today’s advanced video analytics — and how integrators can leverage it to increase revenues.
By Laura Mazzuca Toops, SDM Content Editor
Only a few years ago, the promise of video analytics seemed like more sizzle than steak. Interpretation based on pixel motion and algorithms created false alarms, and the unreliability turned off customers. But over the past two years, advances in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, deep learning, and edge-based IP cameras have made it more accurate than ever before.
Besides traditional security applications, businesses are turning to video data for intelligence purposes, using predictive analytics, patterns and behaviors, which makes video surveillance and video-verified intrusion detection systems more intelligent and capable of more advanced decisions.
The global pandemic lit the fuse for this growth, with businesses demanding analytics on people counting, mask compliance and more. “Over the past two years, we’ve seen a huge demand for video analytics,” says Jason Burrows, regional sales director, Western U.S., IDIS America, Coppell, Texas. In a recent IDIS survey of more than 400 global security professionals, 85 percent of respondents said they were either already using or planning to adopt some type of AI-powered video analytics.
The SDM 2022 Industry Forecast reflects a similar growth pattern: While 52 percent of respondents said they were currently offering video analytics, an additional 33 percent planned to do so within the next one to five years. And current trends suggest that video analytics technology has barely reached its potential.
“With higher demand in IoT and cybersecurity, video analytics will be adopted at a much higher rate,” says Rick Urban, senior product manager, video systems at Identiv, Fremont, Calif. “With the continued merging of video analytics and cybersecurity, new opportunities will open up in whole new markets.”
Quang Trinh, manager, professional services, Axis Communications, Chelmsford, Mass., says that market research groups expect big growth for the video analytics market; the lowest projections are $12 billion by 2027, the highest at $29 billion by 2029. “As more companies invest in AI technologies and deep learning techniques continue to thrive on an abundance of unstructured data, namely the images and video provided by surveillance cameras, growth expectations will increase,” he says.
AI technology has made video analytics more accurate and customizable than ever before. i-PRO’s privacy guard function detects and pixelates faces or persons to prevent individual identification.
PHOTO COURTESY OF i-PRO

“The current market for video analytics is stronger than it has ever been,” says Matthew Cirnigliaro, regional marketing manager, Bosch Security & Safety Systems, Fairport, N.Y. “Analytic features that were once simply sizzle for a demonstration have now matured enough to provide real-world value for users.”
Beyond Simple Motion Detection
For the past 15 years or so, the first generation of video analytics relied on tracking the movements of pixels on a screen — determining within video frames whether something moved in a scene, says Adam Lowenstein, director of product management at i-PRO, Houston. But changes in weather conditions and lighting could skew this simple motion detection method, often resulting in false alarms. “The end user was turned off because it created a lot of false alarms,” Lowenstein says. “People thought [video analytics] made sense, but they were not always sure it was practical for their use case.”
However, over the last two years, a new generation of analytics, supported by AI and machine learning that allows algorithms to recognize known objects, has created dramatic improvements in accuracy. “The emergence and evolution of artificial intelligence and machine learning has led to the development of new video analytics, such as those based on convolutional neural networks [CNN], that lead to higher performance,” says Steffen De Muynck, product manager, security and ITS, Teledyne FLIR, Wilsonville, Ore. “AI in video analytics represents a shift toward smarter, more reliable threat detection solutions with greater classification accuracy, lower false alarm rate, and expanded situational awareness. AI-driven solutions are part of securing a greater return on investment for integrators.”
Video Analytics & AI: Complementary Technologies
We asked our subject matter experts what was the difference in their minds between video analytics and true AI. Here’s how they responded:
“True AI represents a paradigm shift for video analytics, by leveraging artificial intelligence, deep learning, and neural networks. The neural network is the engine that drives AI-powered alarms and notifications, almost acting like a human brain, learning from experience to analyze vast amounts of video data, automatically recognizing objects, places, and movements, and then extracting and storing metadata relating to every scene. This metadata provides classification, identity, and context to video streams, allowing operators to organize, search, and retrieve intelligent information from huge amounts of video footage quickly and easily.” — Jason Burrows, IDIS America
“Sometimes referred to as video content analysis or intelligent video analytics, video analytics use artificial intelligence to complete various tasks by applying computer vision and deep learning to recorded or live video streams. Advances made in deep learning and machine learning, both subsets of AI, have made it possible for video analytics to transform automation that once required human interference to be successfully automated. Artificial intelligence is simply the simulation of human intelligence in machines. AI enables machines to think, learn, and solve problems just like human brains do. AI possesses the power to rationalize like us and take actions to accomplish a goal. With the use of artificial intelligence, machines can execute desired tasks by imitating human intelligence.” — Rick Urban, Identiv
“Artificial intelligence is simply a method for analyzing video. Some other methods include heuristics, machine learning, and even simple motion detection. All these methods for analyzing video have their strengths. For example, AI is great at recognizing known objects. However, heuristics are still superior for detecting completely unknown moving objects. A proper solution may layer both technologies.”
— Matthew Cirnigliaro, Bosch Security and Safety Systems
“The video analytics market is part of the vast video surveillance ecosystem, which includes several different types of video analytics solutions. There are point solutions, focused on solving a specific problem or delivering a single analytic or subset of analytics, such as face or license plate recognition. In addition, there are analytics that are integrated into the offering of a particular VMS or embedded into a camera.”
— Rebecca Law, BriefCam
“It’s about use cases. AI-driven analytics and traditional analytics, like motion based, are both reliable, efficient options, depending on where and what they’re deployed for. We offer both traditional motion-based algorithms as well as AI-based systems. Ultimately, we believe that the future is to be found in an intelligent merger of the two technologies.” — Steffen De Muynck, Teledyne FLIR
“We believe that deep learning AI is the most promising technology for video analytics. We offer AI-based video analytics solutions to customers based on statistical inference engines. This technology, used in combination with a neural network running on the camera at the edge, requires far less calibration (often automated) and can be trained to be much more discriminating in identifying different classes of objects or events.” — Hamish Dobson, Motorola Solutions
//
The global pandemic accelerated advances such as people counting and mask detection, which manufacturers quickly released to market based on the new needs. “The pandemic didn’t change customer demands, but it did expand them,” says Rebecca Law, director of channel management, BriefCam, Newton, Mass. “BriefCam played an essential role in supporting productive and rapid contact tracing, as well as real-time alerting and long-term reporting for mask wearing and physical distancing compliance. Furthermore, it enabled organizations to analyze guest and staff activity via heat maps or data visualizations to determine the most trafficked areas, allowing hotels, casinos, restaurants, theme parks, cruise ships, and others to benchmark desired occupancy norms and to set alerts to prevent overcrowding.”
At the height of the pandemic, businesses like retailers used people counting and queue management to manage staffing and garner business intelligence — and to comply with COVID-19 occupancy and distancing requirements, says Trinh of Axis. Healthcare organizations used touchless access control and video validation to secure restricted areas while also eliminating surface contact with PIN pads to reduce virus spread, he adds.
Fast delivery of analytics solutions to address pandemic needs spurred video analytics companies to roll out new products faster than ever, where in pre-pandemic days, new analytics products took years to release, Lowenstein says.
Big Advantages for Businesses
“Video analytics are a highly flexible technology that can be applied across many different industries,” says Fabio Marti, vice president, marketing at Azena, Pittsburgh, Penn. Logistics and manufacturing use it to monitor and improve operations; retail environments leverage heat mapping to analyze customer flow through stores; and cities across the globe apply video analytics to optimize vehicle traffic flow. Stadiums use it for live monitoring with real-time alerts, such as queue length detection for concession stands during sporting events, and healthcare facilities can leverage fall detection or prevention analytics to protect patients. “This data is not just useful in real time, it’s also optimal for budget and staffing planning to collect specific data over time, such as building occupancy levels, heat mapping in retail settings, or analyzing peak times for passenger volume in a train or metro station,” he adds.
The pandemic helped spur interest in using video analytics for business intelligence. Pictured here is Honeywell Video Analytics’ dashboard detailing people occupancy in a retail environment.
PHOTO COURTESY OF HONEYWELL BUILDING TECHNOLOGIES
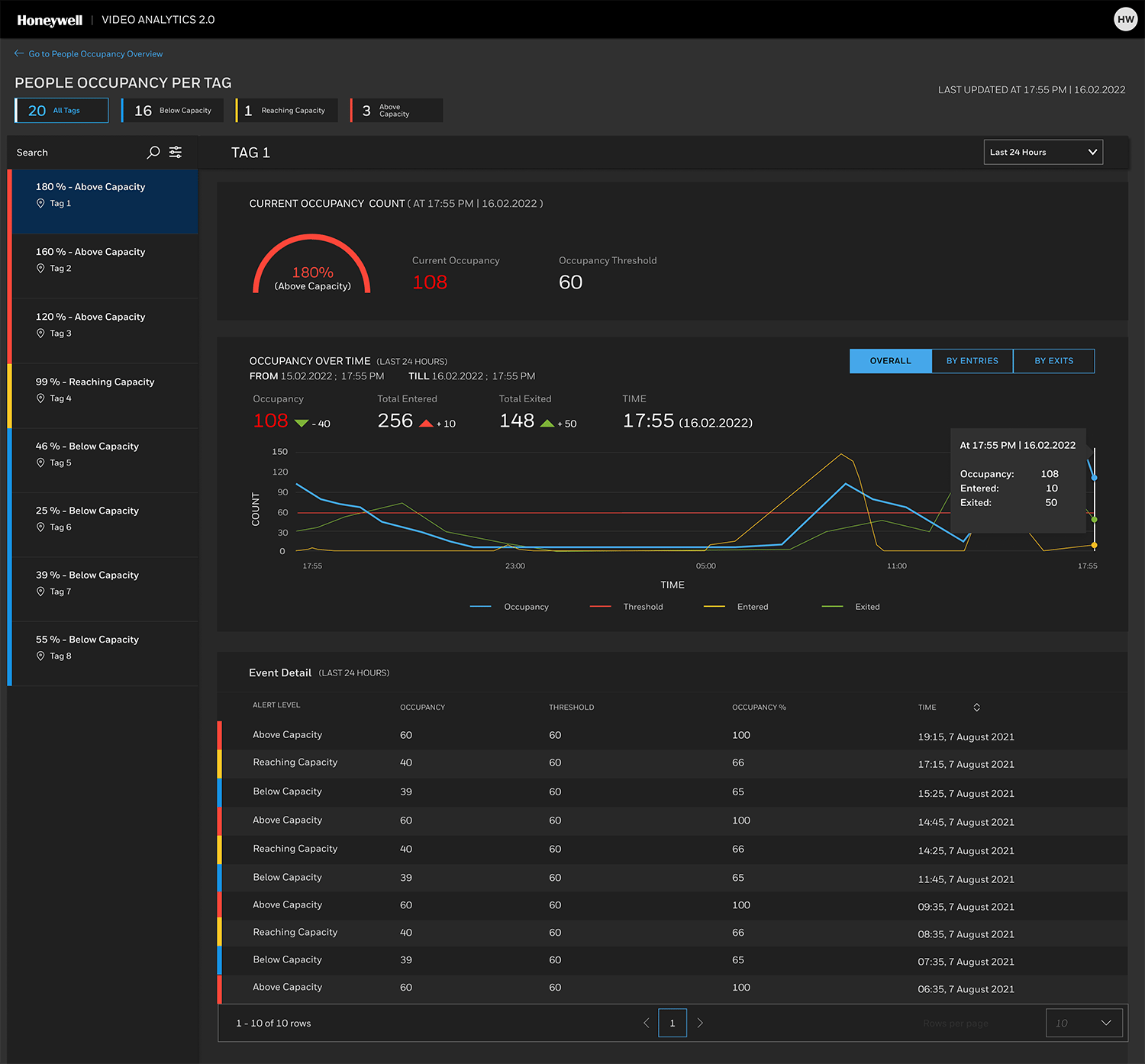
As video analytics applications broaden, end users are demanding more customized solutions tailored to a single purpose, often by adapting existing detection algorithms and retraining models to fit that purpose. “One example is the use of smoke or fire detection analytics to ensure that pumps in an oil field have a constant, clean burning flame to burn off excess gas before it becomes a pollutant,” Marti says. “Another is the deployment of line crossing and object detection analytics in an aquaculture setting to detect and ward off predatory sea birds to prevent fish loss and water contamination.”
Leading the charge for these specialized analytics are AI, cloud, edge cameras and open platforms, which allow users to load third-party analytics from open platform providers onto camera platforms without overburdening the camera with stuff the customer doesn’t need, Lowenstein says. For instance, i-PRO has partnered with third-party analytics providers like Vaxtor (an LPR engine), Databuoy (audio gunshot detection), and others to enhance their end users’ video analytics capabilities.
Robert Oldham, vice president of business development for integrator Stone Security in Salt Lake City, Utah, agrees on the importance of open platforms for video analytics. “It advances the technology quicker and clients can pick the best of breed,” he says. “Our customers prefer and want this.”
But while there’s always a lot of buzz around the power of AI, it is by no means the only tool in the video analytics arsenal, says Bosch’s Cirnigliaro. “AI is a new and exciting tool that is allowing things that weren’t previously possible. However, it certainly isn’t the only tool we have, and others are still very relevant. That’s why Bosch continues to offer all these methods — to provide the most complete solution for as many applications as possible.”
With higher demand in IoT and cybersecurity, video analytics will be adopted at a much higher rate.
— Rick Urban, Identiv
On-Camera Based vs. Software Analytics
Part of video analytics’ tech transformation is attributable to advances in cameras, many of which now are capable of internally performing advanced analytics. “Over the last five years, SOC companies have come up with powerful chip sets that can match the performance of Dell Intel machines and higher GP machines,” says Vijay Dhamija, director of engineering for commercial security, Honeywell Building Technologies, Atlanta. “Cameras are becoming more powerful and can do AI and facial recognition right in the camera. To recognize humans in space, you need good processing power, and cameras can now do that.”
But that doesn’t mean that newer, smarter cameras will necessarily replace servers, he says. “For any new expansions, customers will continue to buy smaller new cameras; but for existing buildings that are not expanding in the near future but still want an analytics solution, they will maintain existing cameras but will gradually replace them with next-gen cameras that are more powerful,” he says. “Both servers and smart cameras are necessary because the total cost of the solution goes down when you start having analytics in the camera. … If you’re investing in smart cameras, the same software will take less resources.”
The Latest Video Analytics Advances
Although AI is the primary driving force behind video analytics technology, our sources pointed to other advances that are revolutionizing this market segment. These include:
- Analytics beyond video: While video provides the sense of sight, analyzing data from the other four senses can provide even better awareness, says Matthew Cirnigliaro of Bosch Security & Safety Systems. “By running audio analytics on cameras, gunshot detection, glass break detection, aggression and distress detection, and even keyword detection can give cameras the ability to provide more complete situational awareness.”
- Edge technology: Smarter cameras that can process data on the edge rather than requiring a server are transforming video analytics. “A year ago, this was just in premium-level cameras for analytics,” says Robert Oldham of Stone Security. “Today, advanced analytics like deep learning and AI are available in low- to mid-tier camera offerings. A $200 camera from a reputable manufacturer has this included at no additional fee. If you can enter the market with a low-cost indoor or fixed lens outdoor camera with advanced analytics included, it means more end users can take advantage of this technology.”
- Lower cost graphics processing units (GPUs): In the past, deep learning required costly hardware to process unstructured data. But over the past five years, the industry is leveraging lower-cost GPUs that can process deep learning algorithms, resulting in more sophisticated deep learning, says Quang Trinh of Axis Communications. “As hardware caught up to the technology, it became more accessible for many companies to run deep learning algorithms,” he says. “Now in our current state, server-based solutions are equipped with CPUs that can run deep learning models and process real-time video for analysis.”
- An expanded app ecosystem: As analytics capabilities improve, more manufacturers will develop specialized and even custom applications. App ecosystems enable the security industry to leverage the third-party developer community, providing more choices for end users, Cirnigliaro says. “The best solutions will rise to the top faster and in a more organic way than if analytics were entirely controlled by a few camera manufacturers.”
//
Urban of Identiv agrees that sometimes both are necessary. “There are basically three models for video analytics: at or near the edge, server-based, or a hybrid solution,” he says. “All three have their advantages and disadvantages.”
For instance, while edge analytics reduce bandwidth usage, certain tasks are still best run on a server, such as license plate recognition, which needs to interface with a large database where plates are stored, cross-referenced, and flagged. Hybrid solutions can deliver powerful analytics at a much lower cost, with camera manufacturers providing space on cameras to allow third-party analytics, which can pass data directly to the server. “The continued evolution of AI and deep learning technologies will accelerate both edge and server capabilities to new levels within the security industry and open new markets for these advanced solutions,” Urban adds.
Others believe back-end analytics are being phased out because of the increased sophistication of cameras. “There’s a big push, and it’s moving faster than anyone expected,” says Oldham of Stone Security. “If you can get deep learning in $200 to $300 price range cameras, it’s a no-brainer. Deep learning is continuously learning and getting better, and analytics are always being trained and getting more advanced.”
Integrators Benefit With RMR
Advances in video analytics are providing security integrators with more opportunities to expand recurring monthly revenue, too. Integrators can leverage the increased value of video analytics to provide improved service-based offerings for their customers, says Hamish Dobson, vice president, product management, video security and access control at Motorola Solutions, Chicago. These can include centralized alarm detection and response services; maintenance services to ensure cameras aren’t obstructed or out of focus; and outsourced search functions when an incident happens and footage needs to be found. “The use of video analytics speeds up these searches considerably and allows integrators to offer this service to their customers at a lower cost,” he says.
Driven by AI and deep learning, video intelligence software detects and extracts objects in video, identifies each object based on trained deep neural networks, and classifies each object to enable intelligent video analytics. Pictured is BriefCam’s video analytics platform hub, highlighting object detection, identification and classification.
PHOTO COURTESY OF BRIEFCAM
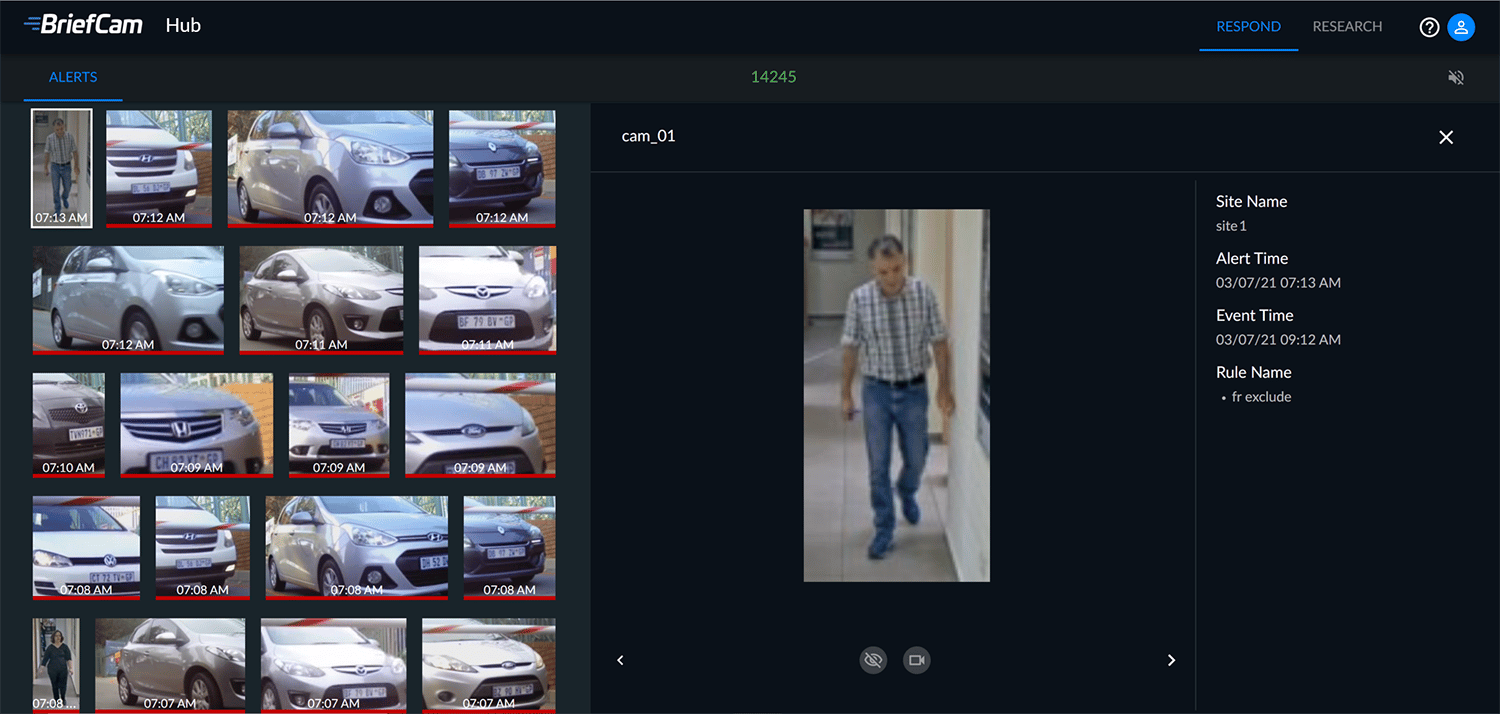
Cirnigliaro of Bosch says there are two primary ways video analytics provide RMR opportunities for integrators: the monitoring model, in which integrators sell video monitoring as a service; and video security as a service, or VSaaS. “In much the same way that we’ve seen the music industry transition from selling individual albums to selling a subscription to a pool of songs, VSaaS allows integrators to sell a surveillance subscription rather than a surveillance system,” he says.
Either way, video analytics can help integrators pivot away from a one-and-done business model.
“Many integrators will sell a video surveillance system, install cameras, then receive most of the money upfront and be done,” says Dean Drako, CEO and founder of Eagle Eye Networks, Austin, Texas. “Cloud is fundamentally an RMR model, generating significant revenue from the customer each year or month to provide the service of recording video in the cloud and running AI on it, or taking care of disc storage. If it’s in the cloud and not on premise, you’re running it, charging a fee, and making more money.”
Tying customers in with more of these services ultimately creates a more valuable business to sell down the road, Drako says. He estimates that RMR businesses are worth 10 times more than those that don’t rely on recurring revenue, with service businesses valued at one to two times revenue, according to investment banking company Imperial Capital.
Deep learning is continuously learning and getting better, and analytics are always being trained and getting more advanced.
— Robert Oldham, Stone Security
An Education Process
Although AI-enhanced video surveillance can deliver increased accuracy and more business intelligence than ever before, integrators must understand its capabilities so they can explain it to their customers — and determine if it’s even the right choice for their unique business needs.
“Overselling or overpromising the capabilities of video analytics as a ‘silver bullet’ is still the greatest pitfall today,” says Urban of Identiv. “Understanding the use case and setting proper expectations from the beginning will provide a much better experience for the end user.”
Dhamija of Honeywell says, “Detection is not the only interest from customers; integrators should look at what problems they’re trying to solve. Analytics is just a small piece of the whole game…. If I can solve a company’s problem by sending video to airport authorities, for example, and closing the loop around alarms, not just generating alarms in a system, that’s more important than just selling analytics to these customers.”
Florian Matusek, product group director for video analytics at Genetec, Montreal, believes the security industries is “too focused on the tech side of things” and should instead prioritize actual customer pain points to deliver the best solution.
“In the end, the technology you use shouldn’t matter to the end user,” he says. “What matters is the outcome.… We’re starting with a solution in search of a problem, and it should be the other way around. Talk to the end user, see what their business problem is, then see how to solve it. Sometimes analytics isn’t the answer. First start with the problem.” SDM
